Motorcycle Basic Technique. Automotive, Basic Technique, Electrical, Machine, Motorcycle, Technology.
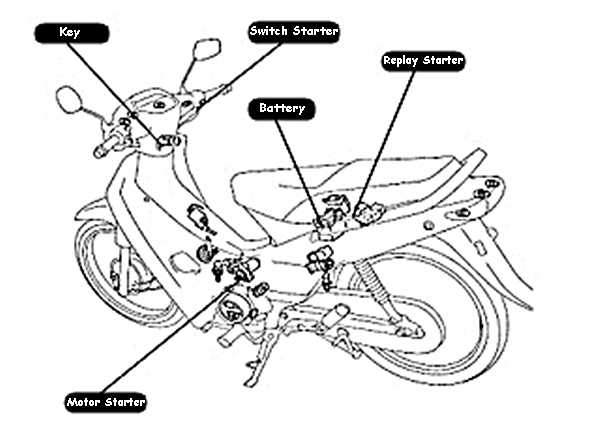
Technology Automotive - Motorcycle Basic Technique - is a guide to understand how to work on motorcycle technique, motorcycle has several main components, each component is divided into several groups on motorcycle engines as in the following discussion. the main component of the motor base consists of several components and consists of several parts, including the frame, and other parts that are combined into one in order to become a motorcycle.
- Machine System
- Electrical System
- Frame / Chassis
Similarly, about the work system on basic motorcycle techniques that I can explain may be useful for you, that's all and thank you. Technology Automotive.